In-depth Analysis of the Ethereum Fusaka Upgrade: Core Changes and Ecosystem Impact
Tanay Ved, Coinmetrics analyst; Translation: @Jinse Finance xz
1. Summary
Scalability Enhancement: Fusaka improves Ethereum scalability by providing higher Blob capacity and a more efficient data availability system through PeerDAS (Peer-to-Peer Data Availability Sampling).
Increased L1 Throughput: Gas limit up to 60 million and execution layer optimizations significantly boost L1 throughput.
Fee and User Experience Optimization: Improvements in the fee mechanism and user experience upgrades lay the foundation for a more unified and cost-effective L1-L2 ecosystem.
2. Fusaka Upgrade Overview
Ethereum plans to conduct its next upgrade, known as "Fusaka," at 21:49 UTC on December 3, 2025 (slot 13,164,544). Fusaka combines the execution layer upgrade "Osaka" and the consensus layer upgrade "Fulu," following the naming conventions of previous forks.
Following the Pectra upgrade in May, Fusaka marks an important step on Ethereum’s scaling roadmap. It enhances layer one performance, expands Blob capacity, improves the cost-effectiveness of Rollups, and brings user experience upgrades. It also introduces the "Blob-Only Parameter" fork mechanism, allowing for safe increases in Blob capacity as Rollup demand grows. Earlier this year, the Ethereum Foundation outlined its "protocol" strategy, centered around three long-term goals: scaling L1, scaling Blob, and improving user experience. Fusaka is the first upgrade to fully align with this unified vision, marking a turning point in how Ethereum plans and improves scalability and accessibility in the future.
This article will outline the key changes of the Fusaka upgrade, as well as its expected impact on the Ethereum mainnet, layer two Rollups, transaction costs, and user experience.
3. Blob Expansion
Last year’s Dencun upgrade introduced "Blob"—a cost-effective solution for Rollups to store transaction data on the Ethereum mainnet. Since then, thanks to the widespread adoption of Rollups such as Base, Arbitrum, and Lighter, Blob usage has often approached saturation (currently near the target of 6 Blobs per block), putting Rollup fees at risk of exponential spikes. The growing demand for data availability has made Blob space a key bottleneck in Ethereum’s scaling path, and the Fusaka upgrade aims to break through this limitation.
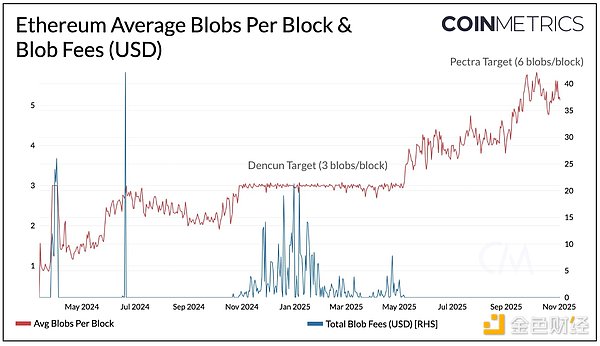
(1) PeerDAS: Peer-to-Peer Data Availability Sampling
PeerDAS (EIP-7594) is arguably the most significant improvement in the Fusaka upgrade, directly aligning with the goal of expanding L1 and Blob capacity. This technology introduces a more efficient data availability verification mechanism for Ethereum nodes: nodes do not need to download the full Blob data but instead verify by sampling fragmented data, reducing the load on L1 consensus nodes while maintaining the same level of security.
Expected impact:
Nodes only need to store about 1/8 of each Blob’s data, allowing for a significant increase in Blob throughput without raising hardware requirements.
Enables Ethereum to safely increase Blob throughput—this is the core driver of Rollup scaling.
Lower data availability costs will reduce L2 transaction fees and improve batch submission reliability.
Lays the foundation for full Danksharding and higher transaction throughput across the ecosystem. For example, Base stated in a blog post that L2 scaling improvements after the Fusaka upgrade could "double chain throughput within two months."
(2) BPO Fork
With PeerDS reducing the bandwidth and storage required for nodes to verify Blob data, Ethereum can now safely increase Blob capacity. The Fusaka upgrade introduces the "Blob-Only Parameter" (BPO) adjustment mechanism, designed to gradually increase the number of Blobs per block. This allows Ethereum to adjust Blob parameters without waiting for a full hard fork, providing the protocol with a more flexible and responsive scaling tool.
Upcoming BPO fork plans:
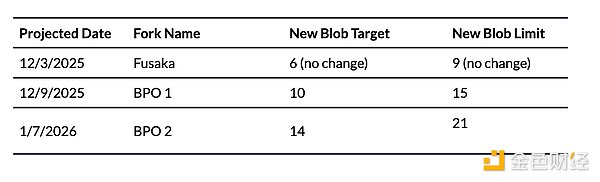
Expected impact:
Increased Data Availability Bandwidth: Gradually increases Rollup capacity per block from 6 Blobs to 128 Blobs, reducing L2 transaction fees.
Achieve Elastic Scaling: Blob parameters can be dynamically adjusted according to demand growth.
Build a Progressive Evolution Path: Aligns with Ethereum’s roadmap to reduce Rollup execution costs and achieve scalable data availability.
(3) Blob Base Fee Adjustment
As Blob capacity expands, Ethereum’s Blob fee market will play a greater role in coordinating Rollup demand. Currently, Rollups spend very little on Blobs. Because demand is relatively insensitive to price and fees cannot be smoothly adjusted with usage, Blob fees often remain at the minimum value of 1 wei. This causes the fee mechanism to be in a "price inelastic" range, limiting its ability to respond to changes in usage.
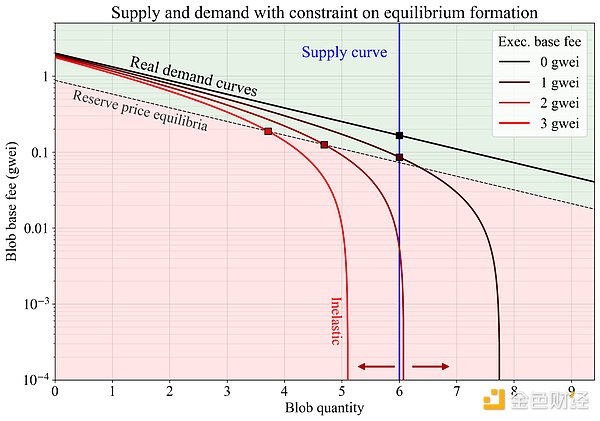
The Fusaka upgrade links the Blob base fee to the L1 base fee, setting a fee floor. This prevents Blob prices from dropping to zero and ensures the fee adjustment mechanism remains effective as Blob capacity expands. Specific impacts include:
More Stable Blob Pricing: Prevents the fee market from falling into a minimum price deadlock.
Predictable Rollup Economic Model: Ensures Rollups pay a reasonable benchmark fee for data availability, avoiding sudden fee volatility.
Minimal Impact on User Costs: Even with the new floor, L2 data costs remain below 1 cent, with negligible impact on user experience.
Sustainable Long-Term Economic Ecosystem: Compensates nodes handling growing Blob traffic. Although current Blob fees contribute little to ETH burning, the future potential is considerable as capacity expands.
4. L1 Scaling
The Fusaka upgrade also places a strong emphasis on L1 scaling. Through the EIP-7935 proposal, it raises the protocol’s default Gas limit to 60 million, significantly enhancing the execution capability of Ethereum’s layer one network. This improvement directly increases the number of transactions that can be included in a single block, resulting in higher throughput, reduced network congestion, and lower Gas fees.
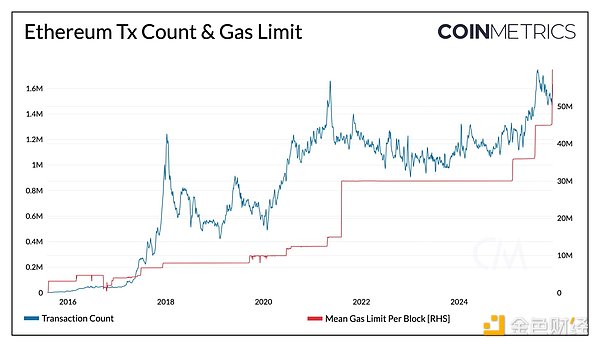
Expected impact:
Increased Throughput: Each block can carry more computation, enhancing overall L1 processing capacity.
Support for Complex Applications: Higher Gas limits provide room for complex contract execution.
Alleviate High-Load Congestion: Additional capacity buffer reduces network congestion during traffic peaks.
Maintain Low Fee Advantage: The expanded network capacity supports the current low Gas fee environment (<0.4 gwei).
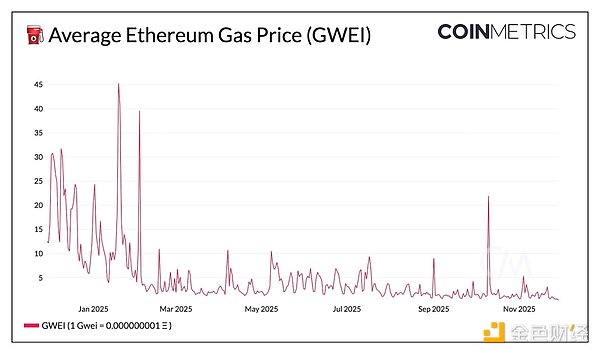
In addition to raising the Gas limit, Fusaka introduces several optimization measures aimed at improving L1 execution efficiency and paving the way for future scaling. Among them, the single transaction Gas usage limit prevents any transaction from monopolizing an entire block and lays the foundation for parallel execution; updates to the ModExp precompiled contract recalibrate Gas costs, setting clearer boundaries for computational operations and ensuring resource consumption remains predictable as throughput grows; the network layer is also streamlined by removing redundant fields from before the Merge, enabling faster Ethereum node synchronization and lighter loads.
5. Optimizing User Experience
The Fusaka upgrade also introduces several updates to enhance usability for developers and end users. EIP-7951 adds native support for the secp256r1 elliptic curve (the signature standard adopted by Apple Secure Enclave, Android Keystore, and most consumer hardware). This will allow wallets and applications to directly integrate familiar authentication processes such as Face ID, Touch ID, and WebAuthn, lowering the barrier for new users while providing stronger security for both retail and institutional users.
These upgrades help modernize Ethereum’s development interfaces and user interaction experience, making it easier to build secure applications tailored to mainstream users.
6. Conclusion
The most direct impact of the Fusaka upgrade will be reflected in reduced Rollup costs, increased Blob throughput, and significant expansion of L1 execution capacity. In the long term, the expansion of Blob space, optimization of costs, and continuous improvement of L1 performance will together shape the economic model of L2 settlement, influence ETH deflation dynamics, and continuously enhance the synergy of the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
Although long-term value ultimately depends on the cumulative degree of demand and adoption, Fusaka lays a clearer and more scalable foundation for Ethereum’s next stage of growth—on this basis, L1 and L2 will be able to collaborate more seamlessly, and the network will be better able to support larger-scale users, assets, and on-chain activities.
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Why is the short seller who made $580,000 now more optimistic about ETH?

The truth behind Bitcoin's overnight 9% surge: Is December the turning point for the crypto market?
Bitcoin strongly rebounded by 6.8% on December 3 to $92,000, while Ethereum surged 8% to break through $3,000, with mid- and small-cap tokens seeing even larger gains. The market rally was driven by multiple factors, including expectations of a Federal Reserve rate cut, Ethereum’s technical upgrades, and policy shifts. Summary generated by Mars AI. This summary was produced by the Mars AI model, and the accuracy and completeness of its content are still in the process of iterative updates.

Even BlackRock can't hold on? BTC ETF sees $3.5 billion outflow in a single month as institutions quietly "deleveraging"
The article analyzes the reasons behind cryptocurrency ETF outflows in November 2025 and their impact on issuers' revenues, comparing the historical performance of BTC and ETH ETFs as well as the current market situation. Summary generated by Mars AI. This summary is produced by the Mars AI model, and the accuracy and completeness of its generated content are still being iteratively updated.
Bitcoin surges to $93K after Sunday flush, as analysts eye $100K
