Interpretation of the Fusaka Upgrade: Scaling, Cost Reduction, Acceleration—Another "Performance Leap" for Ethereum
After Fusaka, will Ethereum usher in a brand new growth cycle?
Original Source: TechFlow
After a weak performance last week, Ethereum spot ETF has once again recorded net inflows, and market sentiment is gradually warming up. Ethereum's next upgrade is already on the way.
Looking back at history, almost every technical upgrade has acted as a catalyst for price, with the improved on-chain performance after upgrades directly reflected in ETH's valuation expectations.
This time, the upcoming Fusaka upgrade on December 3 will be broader in scope and deeper in impact.

It is not just an efficiency optimization, but a major upgrade to the entire Ethereum mainnet: gas costs, L1 throughput, L2 capacity, node thresholds... almost every core indicator that determines the vitality of the network has taken a significant step forward.
If previous upgrades made Ethereum "cheaper" or "faster," the significance of Fusaka lies in making Ethereum more scalable and sustainable.
As protocol functions become increasingly complex, the requirements for the underlying chain's carrying capacity are also rising. With the rise of AI Agents and high-frequency interactive DApps, this upgrade will directly affect Ethereum's position in the next wave of Web3 applications.
So, what exactly has changed? If you want a quick overview, here is a one-picture summary of all the core changes in the Fusaka upgrade:
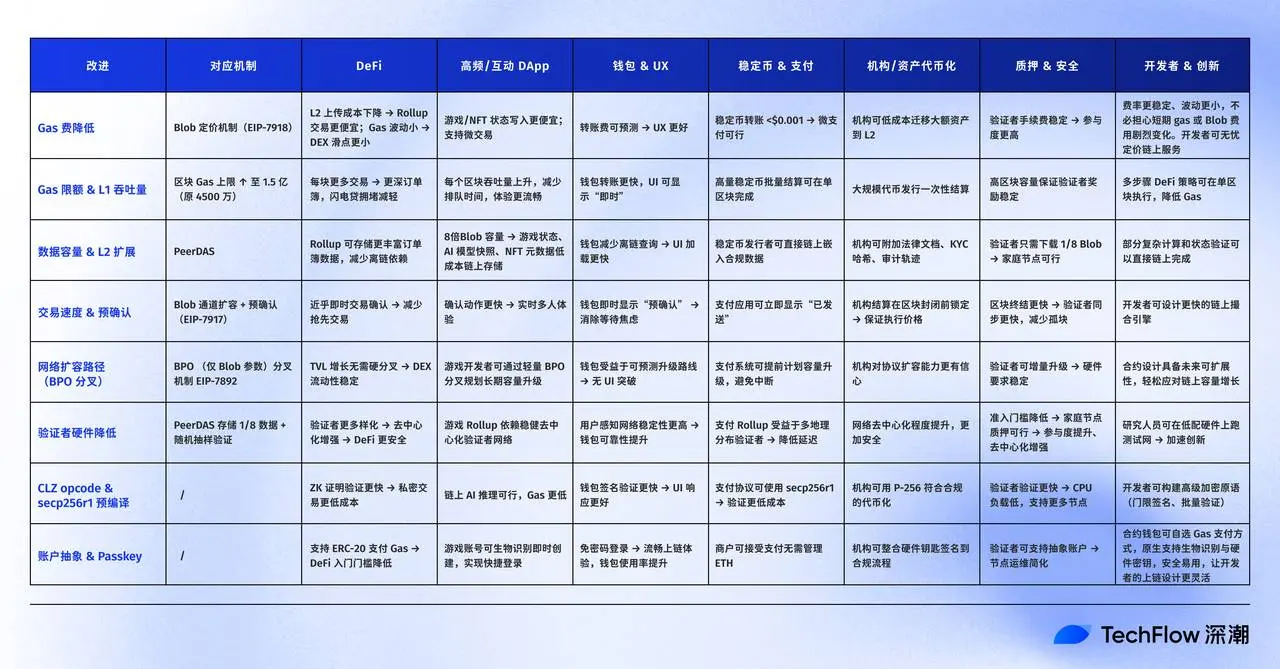
Next, we will popularize the core logic of the Fusaka upgrade from two perspectives: technical aspects and practical impact.
This is definitely not a technical report only for developers. We will explain in a way that even technical novices can easily understand, helping you quickly grasp the key changes behind this upgrade. If you are not interested in the operating mechanism, you can skip directly to the second half to see how this upgrade will affect the Ethereum ecosystem and every user's experience.
Core of the Fusaka Upgrade: Further Scalability
The following technical improvements all have one core goal: to achieve further scalability while ensuring security and decentralization.
PeerDAS: From Full Storage to Sampling Verification
Blob is a new type of data block for Ethereum to store large amounts of on-chain data, packaging Layer 2 transactions into a "big box," much like a courier company delivering many packages at once, efficiently uploading them on-chain without occupying permanent storage space.
Before the Fusaka upgrade, each node had to fully store all data like a courier company storing every package, resulting in overloaded warehouses, bandwidth bottlenecks, and skyrocketing node costs.
PeerDAS proposes a more elegant solution: no more full storage, but network-wide sharding and sampling.
1. Storage: Each blob is split into 8 parts, and each node randomly stores only 1/8, with the rest distributed among other nodes.
2. Verification: Through random sampling verification, the error probability is as low as 1 in 10²⁰–10²⁴. Nodes can quickly retrieve missing fragments using erasure codes and easily reconstruct the complete data.
It sounds simple, but it is a major breakthrough in the field of data availability. This actually means:
- · Node burden drops by 8 times;
- · Network bandwidth pressure plummets;
- · Storage shifts from centralized to distributed, further enhancing security.
Blob Pricing Mechanism
In the Dencun upgrade, Ethereum introduced blobs, allowing Rollups to upload data at lower costs. Their fees are dynamically adjusted by the system based on demand. However, some limitations have emerged in practice:
When demand drops sharply, fees almost fall to zero, failing to reflect actual resource usage.
When demand surges, blob fees can spike instantly, causing Rollup costs to soar and block production to be delayed.
Such drastic fluctuations actually stem from the protocol's inability to perceive the complete price structure, adjusting prices only based on short-term "consumption."
EIP-7918 in the Fusaka upgrade is designed to solve the problem of wildly fluctuating fees. The core idea is to prevent blob fees from fluctuating without limit by setting a reasonable price range.
It adds a layer of minimum reserve price to the pricing system:
· When the price falls below the execution cost threshold, the algorithm will automatically apply the brakes to prevent fees from dropping to near zero;
· At the same time, under high load, it limits the speed of price adjustment to prevent fees from soaring uncontrollably.
Another EIP-7892 makes Ethereum more friendly to Layer2. It allows the network to dynamically fine-tune the capacity, quantity, and size of blobs like turning a knob, without needing a full hard fork for parameter adjustments as before.
When L2 needs higher throughput or lower latency, the mainnet can respond instantly to match these demands, significantly improving system flexibility and scalability.
Security and Usability
Security
Scalability allows Ethereum to process more transactions, but also increases the potential attack surface. DoS attacks, or Denial of Service attacks, can cause network congestion, transaction delays, or even node paralysis, greatly reducing the user experience and security of the entire chain.
Ethereum already has strong anti-DoS design. These improvements are not to fix defects, but to add another layer of protection on top of the existing security framework.

Simply put, if Ethereum is a highway, then the four EIPs of Fusaka are like simultaneously regulating speed (EIP-7823), vehicle weight (EIP-7825), toll fees (EIP-7883), and vehicle length (EIP-7934) on the highway, restricting computational load, single transaction volume, operational costs, and block size from multiple dimensions. This allows for increased traffic while ensuring all vehicles can travel quickly, enabling Ethereum to remain robust, smooth, and resistant to attacks even as it scales.
Usability
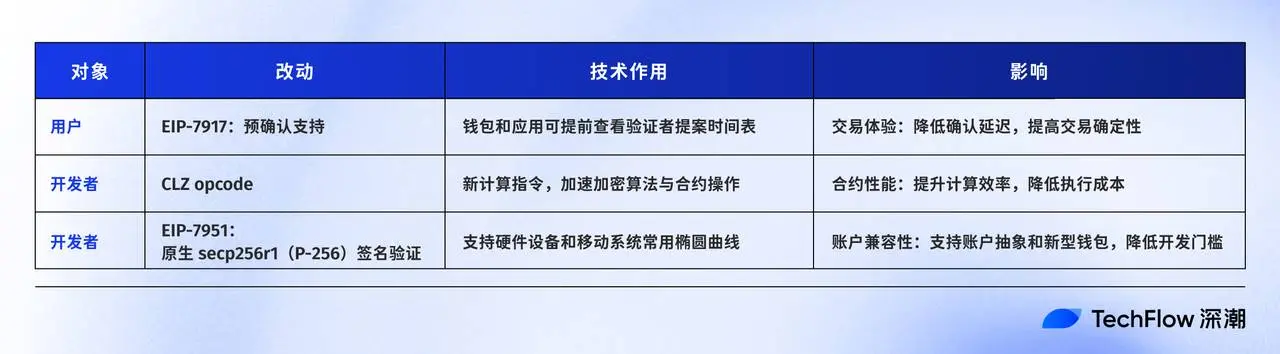
For users, using the highway analogy again: in a nutshell, pre-confirmation means you can reserve a parking spot at the highway entrance, with the exit time locked in before the vehicle enters, so block confirmation is almost instantaneous.
For developers: Fusaka optimizes the execution environment, improving contract computation efficiency, reducing the cost of complex operations, and supporting hardware keys, fingerprint, and mobile device logins, simplifying account management and user interaction.
Practical Impact
Putting technology aside, how significant are the changes to user experience and the ecosystem? Just look at the chart:
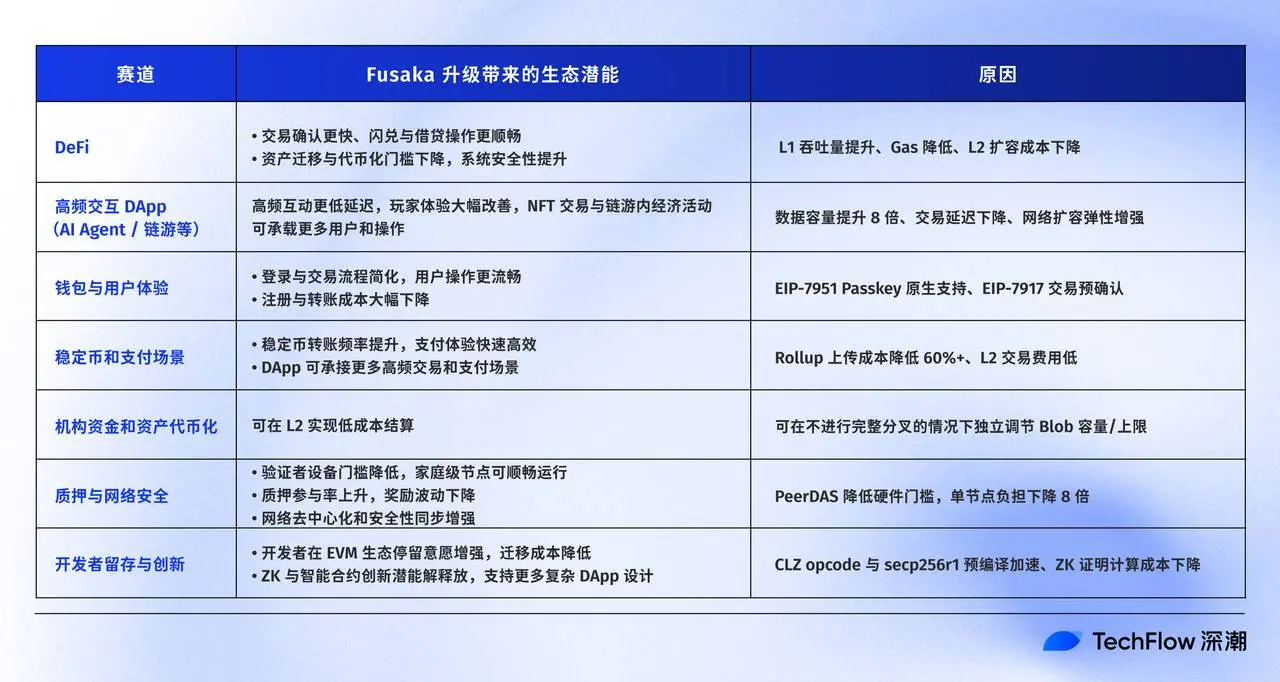
Due to space limitations, here are some points that may be of particular interest, explained in detail:
Staking Will Become Safer and More Stable
In the past, becoming an Ethereum validator was more like a professional sport—high hardware requirements, complex maintenance processes, and data synchronization times that could take days, all of which deterred ordinary users. The Fusaka upgrade is truly bringing this into the "civilian era."
With the launch of the PeerDAS mechanism, nodes only need to download and store about 1/8 of the data fragments when verifying blob data availability, significantly reducing bandwidth and storage costs. What is the result?
Before the Fusaka upgrade, according to the official Ethereum.org blog, a 32 ETH validator could stably run a node on a device with only 8 GB of memory. The upcoming Fusaka upgrade will further reduce the bandwidth and storage requirements for validators. Let's look at the data directly:
· On the Fusaka testnet, the bandwidth required to become a validator node is about 25 Mb/s.
In fact, this device requirement is not high. After the Fusaka upgrade, under good and stable network conditions, more household devices can run Ethereum validator nodes and enjoy native staking rewards.
Fusaka makes home-level nodes a reality—not just professional operators, but more household devices can join network validation, jointly securing Ethereum and directly sharing staking rewards.
This is a true strengthening of decentralization. Lowering the threshold for operation means more independent validators can join, and more validators bring a more stable, more resilient, and more decentralized Ethereum.
From an investor's perspective, this also optimizes the staking risk structure: when validator nodes are no longer concentrated among a few large operators, the chain can remain more stable under high load; volatility decreases, and the yield curve becomes smoother.
High-Frequency Interaction: Fusaka Opens the Era of "Real-Time Ethereum"
In the Web3 world, DeFi, payments, and AI Agents share a common bottleneck: they all require a real-time responsive network.
In the past, Ethereum was secure but not smooth enough. The pace of one block every 12 seconds was sufficient for single large transfers, but for continuous AI Agent command calls or millisecond-level on-chain payment settlements, this pace was clearly too slow.
Fusaka changes all of this.
Through PeerDAS, gas limit expansion, and reduced L2 costs, Ethereum becomes more suitable for high-frequency interactive applications.
We may soon witness a more instantaneous and explosive Ethereum ecosystem.
Let's talk about DeFi in detail here:
Fusaka not only increases throughput but also directly optimizes the DeFi operating experience. Lending, synthetic assets, and high-frequency trading protocols can all "run faster and at lower cost."
Here are some examples of common protocols:
- · Aave: Loan liquidation windows are shortened and liquidation fees are reduced. The reason is that L2 upload costs are lower, liquidation transactions can be packaged faster, reducing slippage and delay risks.
- · Synthetix: Instant settlement time for synthetic assets is reduced, and contract interaction fees decrease. Increased blob capacity means large contract calls are no longer limited, making capital operations more efficient.
- · High-frequency DEX: Liquidity pool depth increases, and large trades no longer cause significant slippage. The driving force behind this is the expansion of block gas limits and lower L2 upload fees, greatly improving liquidity utilization.
Conclusion
The Fusaka upgrade brings enormous potential and may become the most ecosystem-driving, third milestone-level upgrade for Ethereum since Merge and Dencun.
From an 8-fold increase in on-chain data capacity, a sharp drop in transaction fees, several times higher throughput, to lower validator thresholds—all these changes combined will unleash new vitality in the Ethereum ecosystem in this new phase after the Fusaka upgrade.
We should all watch closely: after Fusaka, will Ethereum usher in a brand new growth cycle?
Original link
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
The 12 trillion financing market is in crisis! Institutions urge the Federal Reserve to step up rescue efforts
Wall Street financing costs are rising, highlighting signs of liquidity tightening. Although the Federal Reserve will stop quantitative tightening in December, institutions believe this is not enough and are calling on the Fed to resume bond purchases or increase short-term lending to ease the pressure.
Another Trump 2.0 era tragedy! The largest yen long position in nearly 40 years collapses
As the yen exchange rate hits a nine-month low, investors are pulling back from long positions. With a 300 basis point interest rate differential between the US and Japan, carry trades are dominating the market, putting the yen at further risk of depreciation.
Is a "cliff" in Russian oil production coming? IEA warns: US sanctions on Russia may have "far-reaching consequences"!
U.S. sanctions have dealt a heavy blow to Russia’s oil giants, and the IEA says this could have the most profound impact on the global oil market so far. Although Russian oil exports have not yet seen a significant decline, supply chain risks are spreading across borders.
Leading DEXs on Base and OP will merge and expand deployment to Arc and Ethereum
Uniswap's new proposal reduces LP earnings, while Aero integrates LPs into the entire protocol's cash flow.